Automotive products: Market overview, data sources, and regional leaders
The automotive products market, spanning car and motorcycle parts, accessories, consumables, tools, and tires, is vast, resilient, and increasingly digital-first.
The automotive industry is a complex ecosystem shaped by many factors — from regional nuances and economic conditions to consumer income levels, local regulations, brand loyalty, and supply chain logistics.
Success in this field depends on understanding and adapting to these peculiarities. Some challenges — like navigating international regulations or managing global supply chains — are inherently complex. Others, however, can be effectively addressed with data-driven decisions.
The key? Getting the right data.
Collecting market intelligence manually — for example, monitoring competitors’ spare parts prices — can be exhausting and counterproductive, especially when dealing with hundreds of thousands of SKUs across multiple regions.
This is where comprehensive datasets become a game-changer. They allow manufacturers, distributors, and retailers to make decisions based on facts, trends, and logic, rather than on guesswork.
In business terms, a dataset is a structured collection of information gathered from one or more sources. In the automotive industry, datasets can include:
When sourced and updated regularly, datasets form the foundation for market analysis, competitor benchmarking, and strategic planning.
A Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) policy is an agreement between a manufacturer and its retailers stipulating that the retailer will not advertise a product below a certain pre-set price.
Example in automotive context: A tire manufacturer enforces a MAP policy to ensure its premium tires are not advertised at bargain-basement prices online. This helps sustain the perception of quality and keeps pricing aligned across different retail channels.
Monitor both OEM and generic alternatives.
Example: A major vehicle and parts manufacturer wants to track over 400,000 products across 20+ countries, focusing on 1–2 key online spare parts marketplaces in each country. By partnering with a data provider, they can automatically track market changes, detect pricing shifts, and adjust strategies.
Track the price of the same product across multiple marketplaces and countries.
Example: A popular shock absorber sells for €120 on a German marketplace but €150 on a French one. The manufacturer uses this data to adjust its pricing strategy and ensure competitiveness without eroding margins.
Identify differences in pricing, product availability, and demand between domestic and international markets.
Example: A European retailer uses datasets to compare spare parts prices in Eastern vs. Western Europe, finding significant gaps in aftermarket brake pad pricing — and using this insight to source more cost-effective suppliers.
Demand for certain vehicle models or spare parts often depends on regional income levels and economic conditions.
Example: In high-income markets, premium alloy wheels may be in high demand, while in emerging markets, affordable steel wheels dominate sales. Datasets reveal these patterns so companies can tailor stock accordingly.
Spot gaps in product availability or unmet demand.
Example: Data analysis shows that in Southeast Asia, there’s growing demand for hybrid vehicle components, but local suppliers offer limited stock. A retailer moves quickly to fill the gap.
Accurate data helps plan stock levels to avoid overstocking or shortages.
Example: A distributor notices seasonal spikes in demand for winter tires across Northern Europe and adjusts its ordering cycle accordingly.
Understanding market share helps manufacturers and retailers evaluate competitive positioning.
Example: An automotive battery manufacturer tracks market share data quarterly and notices a consistent drop in one region due to a competitor’s aggressive marketing — prompting a timely promotional campaign to recover ground.
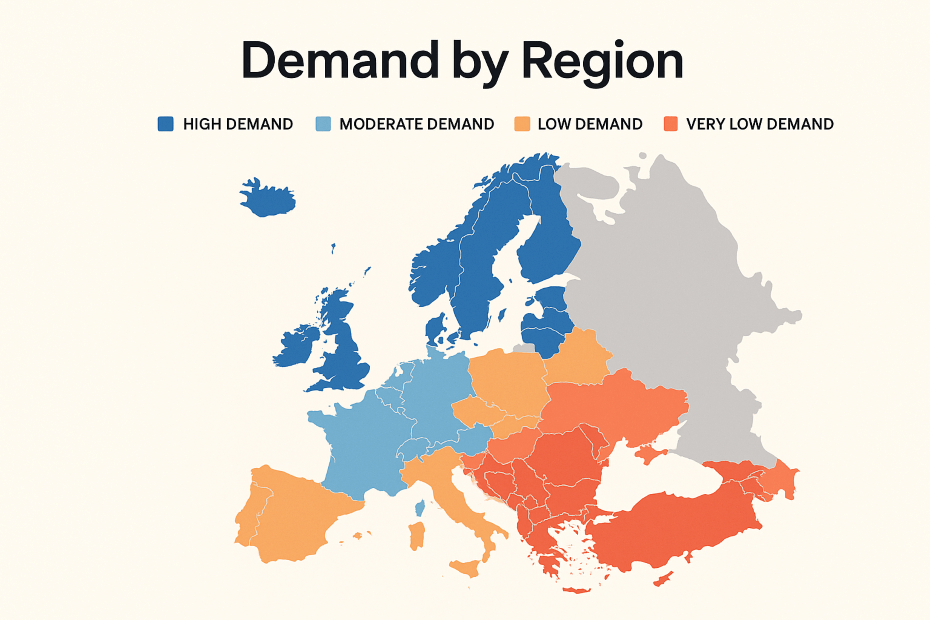
Analyze which regions have the highest and lowest demand for specific parts or models.
Example: Data shows that electric vehicle charging cables are in high demand in Northern Europe but have low adoption rates in parts of Southern Europe. This insight guides targeted marketing and distribution.
Leverage customer feedback to improve products, service, and marketing messages.
Example: Sentiment analysis of reviews for a specific brake pad model shows recurring complaints about noise. The manufacturer uses this insight to update the design and highlight the improvement in marketing campaigns.
When building datasets, businesses can gather data from both international and local marketplaces, depending on their target regions.
International sources:
Regional / Local sources:
These sites can be monitored for pricing, availability, product specifications, reviews, and promotions, forming the backbone of competitive analysis datasets.
SSA Group is a reliable and experienced provider of datasets and web crawling services for the automotive industry.
We deliver custom, high-quality datasets tailored to your business needs — including preferred data sources, required attributes, delivery formats, and flexible update frequencies.
A client from the Netherlands, Motorcycle Spare Parts, runs an e-commerce shop specializing in identifying and selling motorcycle spare parts through technical drawings.
SSA Group’s data crawling solution enables them to keep their massive inventory updated and competitive.
In the competitive automotive sector, success depends on understanding your market and acting faster than competitors. High-quality datasets give you the insights you need to make informed, profitable decisions — from pricing and inventory management to market expansion strategies.
To request a custom dataset, visit the SSA Datasets page.
If you’re looking for a ready-made, ready-to-use automotive dataset for your AI or BI solutions, explore Datasets.store — a webstore offering structured datasets across multiple automotive categories.

The automotive products market, spanning car and motorcycle parts, accessories, consumables, tools, and tires, is vast, resilient, and increasingly digital-first.
The Beauty & Personal Care market is rapidly evolving — fragmented across private-label drugstores, prestige specialists, and fast-scaling e-commerce platforms.
you're currently offline